Are you planning to start a startup but confused between Technical startup and Non Technical startup? For either, there is a neck breaking competition in the outside world, howbeit, there still are many who bite the bullet and come up with million-making businesses. Most of the times, the answer about the scope of a business idea resides in the place where one plans to start the business from. Some cities in India favour the growth of technology while some will boost a non-technical initiative. There is scope for either in any place where the business idea fits and is required; yet, the pace of growth would vary in accordance with the environment.
The requirement of city people and amenities that the vicinity provides plays a crucial role in this stance, for example, businesses require manpower, some raw material, computers, and many other things depending on the kind of enterprise it is. Researchers help to clarify whether the business idea can be started in that place. The other thing that holds prominence here is where the final product can be supplied? Reaching clients is the soul of business, if the environment doesn’t allow a proper communication, then the business might collapse.
Here, in this article, you will get an answer to this major question that many people have asked regarding scopes of the two kinds of businesses in India. We hope your queries are well responded well.
Let’s first differentiate what kind of startups are known as Technical Startups and what kind of startups are known as non-technical startups.
Types of Technical Startup
- IT Hub
- Robotics Industry
- Mechanical Industry
- Telecommunication Industry
- Medical Industry
- Biotechnology Industry
- Space and Research Industry
Types of Non-Technical startup
- Educational Industry
- Food chain Industry
- Real estate or construction business
- Agriculture Industry
- Service Industry
- Media Industry
- Mining Industry
Now let’s have a look on the scope of the success of technical startups vs non-technical startups depending on few important parameters of business.
1. PROTOTYPE
This is the very first phase in a business development when just founder and co-founder work on their startup and presents business in a small model.
A technical startup can be initiated from a small room as well as, large area isn’t a compulsion here. Taking an example from IT hub, Flipkart founder and co-founder, initially developed a website for their online bookstore in a room and later on, when they start getting successful, they expanded their business. Currently, they are having so many offices around the globe. Though, all the research work regarding robots, medicines, biotechnology or spaces are done in labs. In these industries too, the area required is less. Hence, so the funds are required by technical startups in this phase aren’t much.
From the prototype phase onwards, Non-technical startups require a large amount of area. A Large area is the basic need of non-technical startups. If we look at these non-technical industries, educational industry required large land for building their school chain, food chain business required large land for hotels and same is with real estate business, agriculture industry and Mining industry. They all require large area except service industry. Service industry can be started from a room. Due to the requirement of large area, investment is quite high in this phase.
2. FUNDING
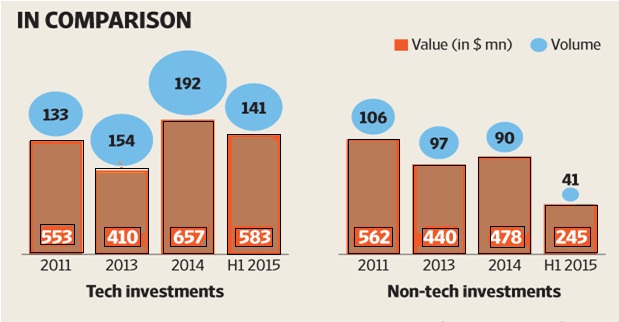
Source- Venture Intelligence
Funding is one of the major factors for a business’s success. As you have to convince a rigid third party for to invest his/her highly valued money in your idea, by making them believe in you and your idea.
The success rate of a technology startup is quite high as compared to non-technical startup, that’s the reason technical startups easily attract the venture capital.
Evidence of investments by Venture Capital is the research report of Venture Intelligence, Chennai. According to the report, the investments in the non-tech startups are constantly tampering off from the year 2011 to 2015.
If we see the record of 2015 in the graph, 141 tech startups got funding of $583 million whereas, at the same time, just 41 non-tech startups got funding which was $245 million. The source for this graph is Venture Intelligence.
From these records, we can conclude, non-technical startups face many struggles and have to work really hard to get funds in comparison to technical startups.
Related- How to Raise Initial Funding?
3. Hiring Candidates
In a Technical startup, technical work is more as compared to manual work. People with good technical knowledge very rarely join the non-established startup companies. They prefer to seek job security. So, Startup companies in beginning usually get people with weak programming concept. Hiring strong candidates is important for a startup company but it’s a tough deal to select one. Candidates have to go through various phases of the interview to get selected. Technical startups have to hire them at a good pay scale. After hiring, there is a requirement of 4-5 months training period to those candidates. Employee availability is tough for technology startups but once the employees join them, they will remain with them for a long period
If we look at the stats:
- 46% of the new hires fail to achieve the goal or fulfill the tasks within the first 18 months. The reason for failure is not the skills but the attitude and culture problem.
- It has been seen that a great developer is 10x more efficient than an average developer.
In a non-tech startup, manpower is highly required. Without manpower, non-technical startups can’t run. There is no barrier of qualifications for joining a non-tech startup. Even, the illiterate candidate can also join it. Candidates get wages on the basis of their work per day. Employee availability is quite fast in it but the rate of getting employees is near about same as the rate of losing them. Employees prefer to join another job (if they get) at higher wages. If we talk about people management, it’s comparatively poor as illiterate or less educated people work here.
4. Management
In technical startups, all the employees are well educated. They know the etiquette of behaving in office. The manager doesn’t find much difficulty in maintaining the office decorum.
In non-technical startups, most of the employees are literate or illiterate. They don’t know how to talk with manners with each other and how to behave properly. It has been seen that labors used to fight with each other at the site. Labor strike for wage increment is a common problem faced by non-technical startups. Management finds really tough to handle these situations.
5. Media Coverage
For the technical startup, it is necessary to maintain their good image in the media and keep an eye on their reviews too. It has been seen that 75% of the people around the world look at the reviews before buying a product or using any service. Media coverage plays a vital role in their success, they can’t run without media. People are highly influenced by looking at the positive/negative reviews regarding product/service of the particular startup in media. Successfully established technical startup can be easily beaten off by other technical startups (if it’s good) in the same field in a short span of time.
At the same time, non-technical startup very rarely covered by the media. They prefer the traditional way of customer acquisition than digitization. They take months or years to establish themselves as successful and once they establish, it’s hard for others to beat them off in a short span of time. The biggest example of a non-technical startup is Patanjali.
If we look at the stats the 56% small non-technical startups expect to grow revenue by improving existing customer experience.


![12 Ways to Increase Profits of Your Business [2021]](https://www.businessalligators.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/girl-working.jpeg)


nicely written point by point and awesome stats collection…. very informative 🙂
Nice article, covers the major aspects well!
This article is really great!!
Very informative …….nice work……perfect scenerio ..interesting in reading
An insightful comparison! This blog helps aspiring entrepreneurs understand the distinct advantages and challenges of both technical and non-technical startups, making it easier to make an informed decision based on their strengths and interests.